+46.8 Million
Population
10th
Largest Country in Africa and 10th Largest in the World
+2,381,741
Square Kilometers
Get Ready to Started?
Algeria
Country Overview
Algeria, the largest country in Africa and the 10th largest in the world, is a hidden gem that remains largely unexplored by tourists. Despite its vast size, which could almost fit Alaska and Texas combined, its hidden gems and tranquil beauty have yet to be discovered by the masses, with 2.4 million visitors in 2019, ranking 111th in the world.
Algeria is a country of rare beauty, with a pristine Mediterranean coastline, fertile green highlands, snow-peaked mountains, and the majestic Sahara down south. It is a continent in itself, waiting to be explored by the adventurous traveler.
Geographic Location
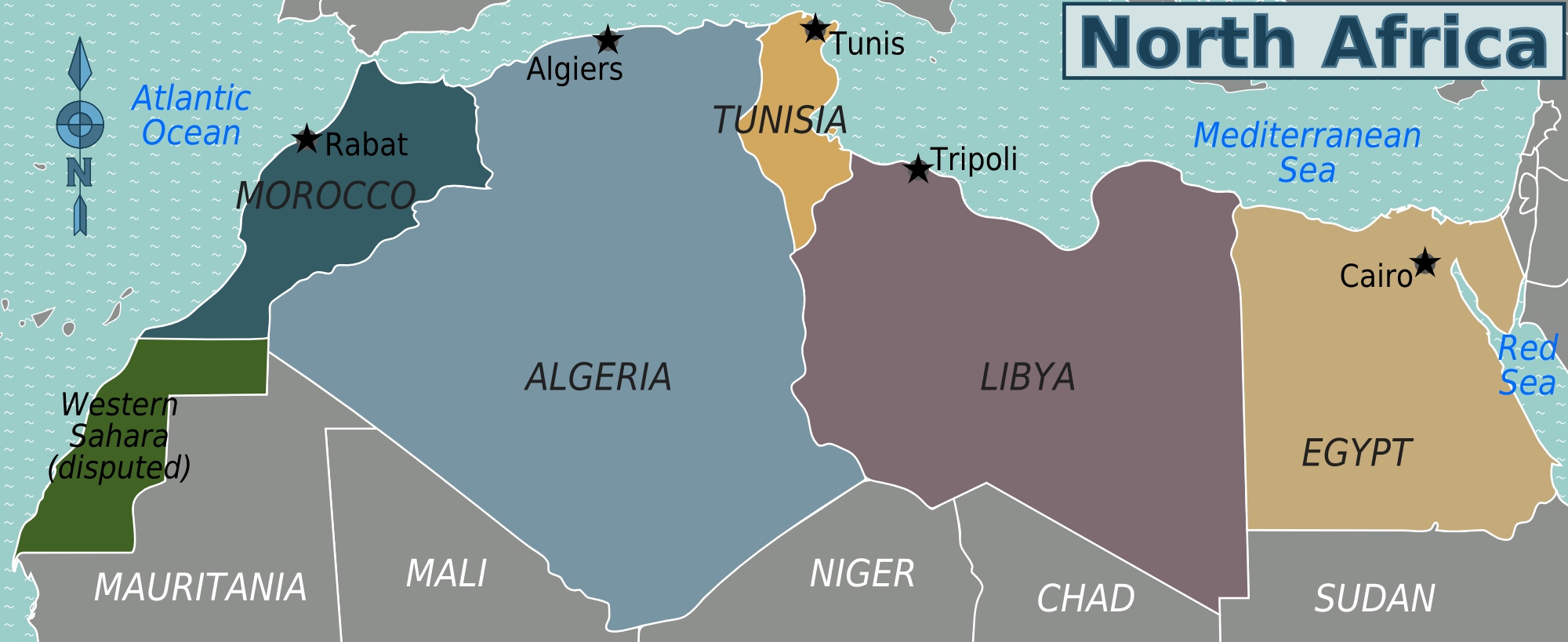
Algeria is located in North Africa, with a coastline along the Mediterranean Sea. It shares its borders with Tunisia to the northeast, Libya to the east, Niger to the southeast, Mali to the southwest, Mauritania and Western Sahara to the west, and Morocco to the northwest.
Map showing Algeria’s location in Africa. By Sanjay Rao
Getting Around
Major and Minor Airports:
- Houari Boumediene International Airport (Algiers): The main international gateway, located in the capital city, serving both domestic and international flights.
- Ahmed Ben Bella International Airport (Oran): Serving the coastal city of Oran, handling domestic and international flights.
- Constantine Mohamed Boudiaf International Airport (Constantine): A key airport in eastern Algeria, connecting domestic and international destinations.
- Annaba Rabah Bitat Airport (Annaba): Primarily serving domestic flights and some international routes to neighboring countries.
- Tamanrasset Aguenar Airport (Tamanrasset): A smaller airport serving southern Algeria, connecting to Saharan cities and offering domestic flights.
Flying Times to Algeria:
Here are approximate flying times to Algeria from major global hubs:
- From Europe:
- London: Approximately 2–3 hours
- Paris: Approximately 2–3 hours
- From Asia:
- Dubai: Approximately 6–7 hours
- Tokyo: Approximately 15–16 hours
- From North America:
- New York: Approximately 8–9 hours (with layovers)
- Toronto: Approximately 9–10 hours (with layovers)
- From South America:
- São Paulo: Approximately 13–14 hours (with multiple connections)
- From Africa:
- Johannesburg: Approximately 9–10 hours (with layovers)
- Cairo: Approximately 2–3 hours
- From Oceania:
- Sydney: Approximately 20–22 hours (with multiple connections)
Popular Cities:
- Algiers: The capital city, often referred to as Algiers the White” for its sunlit, gleaming white buildings.
- Oran: A lively coastal city, known for Rai music.
- Constantine: Famous for its dramatic bridges.
- Tlemcen: Rich in Islamic heritage and architecture.
- Ghardaia: A unique Saharan UNESCO site.
Transportation: Algeria has a well-developed transportation network, with air, land, and sea options available. The country has several international airports, with Algiers International Airport being the largest and busiest. The national carrier, Air Algerie, operates flights to several domestic and international destinations. The country’s road network is extensive, with several highways and expressways connecting the major cities. The railway network is also well-developed, with several trains connecting the major cities. The country has several ports, with Algiers Port being the largest and busiest. Ferries connect Algeria to several European countries, including France, Italy, and Spain.
Did You Know?
Algeria is home to seven UNESCO World Heritage Sites, including the ancient Roman ruins of Timgad and Djemila, which showcase some of the best-preserved Roman architectural legacies in North Africa.
Popular Destinations
- Algiers: The capital city, famous for its historic Casbah, French colonial architecture, and Mediterranean coastline.
- Oran: A bustling coastal city known for its beaches, vibrant culture, and Rai music heritage.
- Annaba: A picturesque coastal city featuring stunning views and the historic Basilica of St. Augustine.
- Timgad: A UNESCO World Heritage site showcasing some of the best-preserved Roman ruins in North Africa.
- Djemila: Another UNESCO-listed Roman city, celebrated for its well-preserved temples, basilicas, and forums.
- Timimoun: A striking Saharan oasis town, known for its red adobe architecture and dramatic desert landscapes.
- Constantine: The “City of Bridges,” offering breathtaking views of dramatic gorges and a rich history.
- Hoggar Mountains (Tamanrasset): A stunning Saharan mountain range, perfect for adventure and photography enthusiasts.
Social and Cultural Insights
People and Society: Algeria has a diverse population, with Arabs, Berbers, and Europeans making up the majority of the population. Arabic is the official language, widely used in education, government, and daily life, while Berber (Tamazight) is also recognized as a national language and is spoken by many, particularly in rural and mountainous regions. French, a legacy of Algeria’s colonial history, is commonly used in business, academia, and media.
The society is predominantly Muslim, with Islam being the state religion. Algeria has a young population, with more than 60% of the population under the age of 30. Algerian society is collectivist, with a strong emphasis on family and community. Hospitality is an important societal norm, and guests are treated with great respect and generosity. Progress has been made in enhancing women’s rights, with ongoing initiatives aimed at achieving full gender parity in education and employment.
Culture: Algeria’s culture is a rich tapestry of Arab, Berber, and French influences.
- Traditional music, art, and cuisine are an integral part of the country’s cultural heritage. The country’s music scene is diverse, with genres ranging from classical Arabic music to modern pop and rock.
- The country is also home to several festivals and events, such as the International Film Festival of Algiers, the Algiers International Book Fair, and the Sahara International Marathon.
- Art is also an important part of Algerian culture, with traditional crafts such as pottery, weaving, and metalwork being highly valued.
- Algerian cuisine is a fusion of Arab, Berber, and French flavors, with dishes such as couscous, tagine, and merguez sausage being popular.
Cultural Etiquette and Tips: Algerians value politeness and respect in social interactions. Greetings often involve handshakes and kind words, with “Salam” or “Bonjour” being common ways to start a conversation. Modest clothing is encouraged, especially in rural areas or religious spaces. Hospitality is a cornerstone of Algerian culture, so don’t be surprised if you’re offered tea or a meal when visiting someone’s home. It’s polite to bring a small gift, like pastries or fruit, as a token of appreciation. Asking permission before photographing people or religious sites is always recommended.
Public Holidays:
- New Year’s Day: January 1
- Labor Day: May 1
- Independence Day: July 5 (celebrating Algeria’s independence from France in 1962)
- Revolution Day: November 1 (marking the start of the Algerian War of Independence in 1954)
- Eid al-Fitr: Date varies (celebrating the end of Ramadan)
- Eid al-Adha: Date varies (Festival of Sacrifice)
- Islamic New Year (Hijri New Year): Date varies
- Mawlid al-Nabi: Date varies (commemorating the birth of Prophet Muhammad
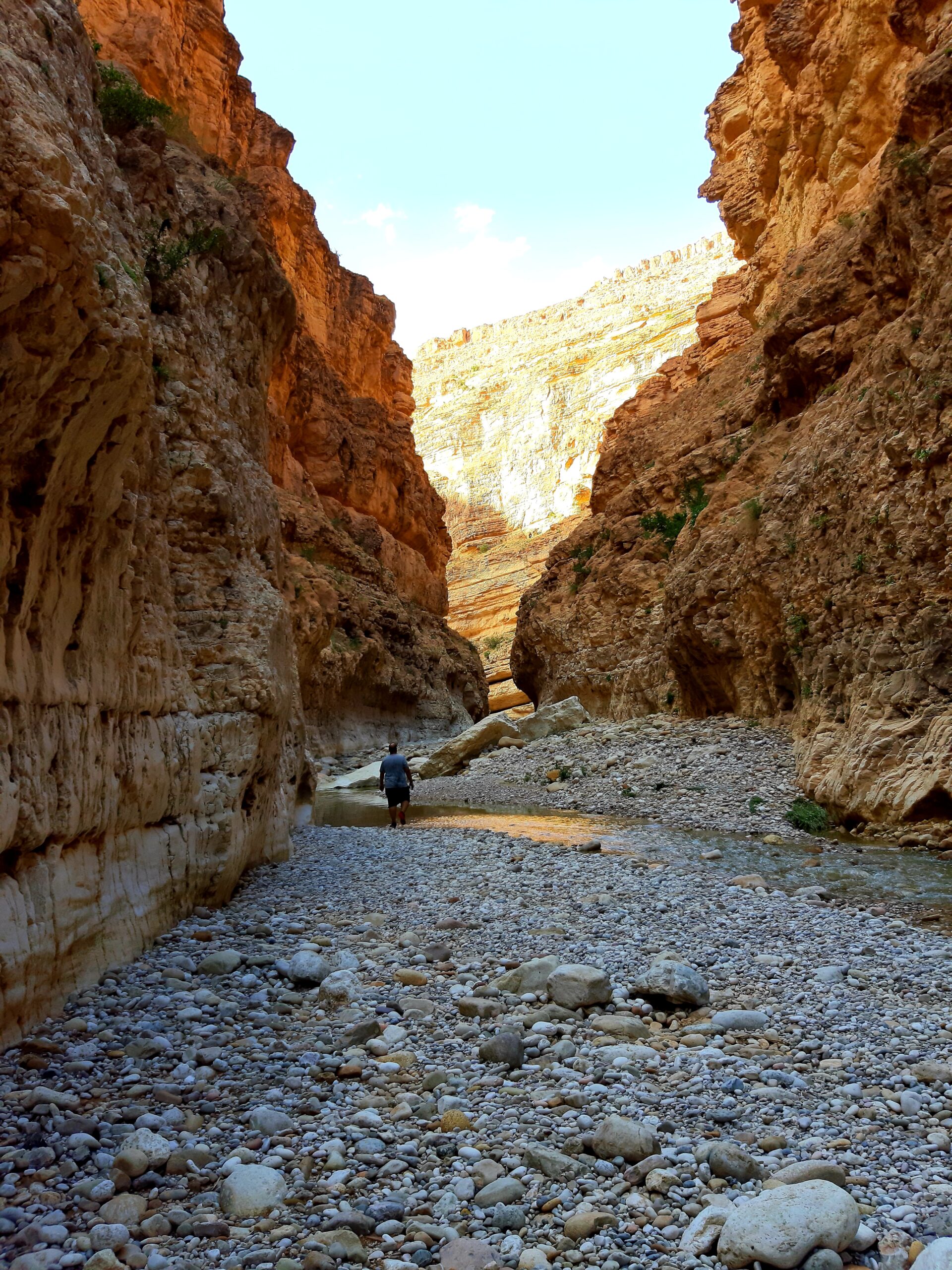

M’Chounech Mountains, Biskra, Algeria. Photo by Omar Karim Chehaba.
Climate and Natural Highlights
Climate: Algeria’s geography gives rise to a mix of Mediterranean, desert, and mountain climates. Coastal regions enjoy mild winters and hot summers, typical of a Mediterranean climate. In contrast, the Sahara experiences extreme heat, with summer temperatures often exceeding 40°C. The mountainous areas are cooler, with occasional snowfall in winter.
The best time to visit depends on your destination and activities. Coastal areas are ideal in spring and fall, while the desert is more comfortable in winter and early spring.
Sunrise and Sunset Times: Due to its location along the Mediterranean coast and the vast Sahara Desert, Algeria experiences seasonal variations in sunrise and sunset times. In summer, the sun typically rises around 5:30 AM and sets around 8:00 PM, while in winter, sunrise is around 7:30 AM and sunset at 5:30 PM.
Wildlife and Natural Landscapes: Algeria’s landscapes range from the vast Sahara Desert to the rugged Tell Atlas Mountains and the dramatic Ahaggar Mountains, known for their scenic beauty and trekking opportunities. The Tassili n’Ajjer National Park, a UNESCO site, stands out for its prehistoric rock art and unique desert terrain. While Algeria is not as wildlife-rich as other African nations, it is home to distinct species like the fennec fox and Barbary macaque. The coastal wetlands also attract migratory birds, adding to the country’s ecological diversity.
Economic and Political Overview
History: Algeria has a rich history that dates back to the Phoenician period. It has been home to various civilizations, including the Numidian Berber kingdoms, the Roman Empire, the Muslim Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the French colonial empire. Each of these civilizations has left its mark on Algeria, contributing to its diverse cultural heritage. On July 5, 1962, Algeria gained independence from French colonial rule, marking the end of over 130 years of colonization
Government and Politics: Algeria is a presidential republic, with the President serving as both the head of state and the head of government. The President is elected for a five-year term and can serve a maximum of two terms. The government is responsible for managing the country’s affairs, while the Parliament, consisting of the National People’s Assembly and the Council of the Nation, is responsible for making laws.
Economy: Algeria’s economy is heavily dependent on the oil and gas sector, which accounts for more than 95% of its exports. The country has the 10th largest reserves of natural gas in the world and is a major exporter of liquefied natural gas. However, the government is working to diversify the economy by investing in other sectors, such as agriculture, tourism, and manufacturing.
Safety, Health, and Entry Requirements
- Safety and Travel Advisories: Algeria is generally a safe country for tourists, but it is important to exercise caution and follow local laws and customs. The country has a low crime rate, but petty crimes such as pickpocketing and theft can occur. It is important to avoid displaying valuables and to keep a close eye on your belongings. The U.S. Department of State encourages travelers to be well-informed and exercise standard precautions when visiting Algeria, as they would in any international travel, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.
- Healthcare and Vaccinations: Algeria has a well-developed healthcare system, with several hospitals and clinics located throughout the country. It is important to have travel health insurance that covers medical expenses, as medical costs can be high. It’s recommended to carry a sufficient supply of prescription medications to ensure your health needs are met throughout your stay, providing peace of mind as you explore. It is also recommended to be up-to-date on routine vaccinations.
Visa Requirements and Entry Procedures: Algeria requires a visa for most foreign nationals, including U.S. citizens. It’s advisable to begin the visa application process early, allowing ample time to secure your entry. More information can be found on the Algeria embassy or consulate website in your country of residence.
Note that independent travel to Algeria requires permits, guides, and police escorts, especially for travel outside of the Mediterranean coastline. For a more seamless experience, you might consider using a travel agency.

Region
- North Africa
Capital City
- Algiers, also known as "La blanche"
Currency
- Algerian Dinar (DZD)
Languages
- Arabic
- Berber
- French
Timezone
- Central European Time (CET), UTC+1
- United States

